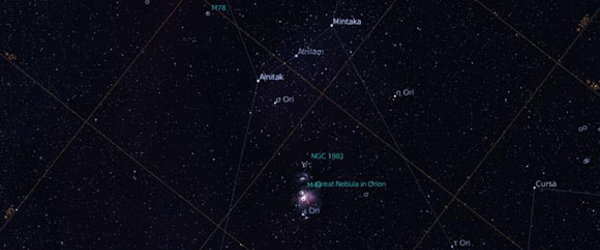
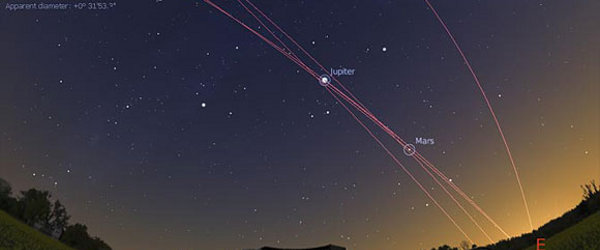
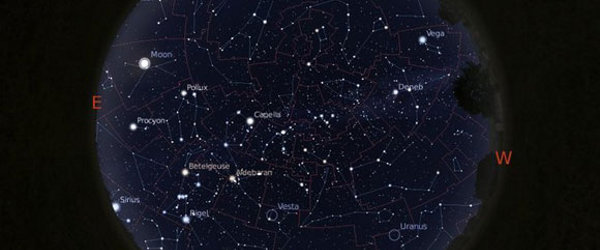
Stellarium is a free open source planetarium for your computer. It shows a realistic sky in 3D, just like what you see with the naked eye, binoculars or a telescope.
features
sky
- default catalogue of over 600,000 stars
- extra catalogues with more than 177 million stars
- default catalogue of over 80,000 deep-sky objects
- extra catalogue with more than 1 million deep-sky objects
- asterisms and illustrations of the constellations
- constellations for 40+ different cultures
- calendars of 35+ different cultures
- images of nebulae (full Messier catalogue)
- realistic Milky Way
- very realistic atmosphere, sunrise and sunset
- the planets and their satellites
- all-sky surveys (DSS, HiPS)
interface
- a powerful zoom feature
- time control
- multilingual interface
- scripting interface
- fisheye projection for planetarium domes
- spheric mirror projection for your own low-cost dome
- graphical interface and extensive keyboard control
- HTTP interface (web-based control, remote control API)
- telescope control
visualisation
- several coordinate grids
- precession circles
- star twinkling
- shooting stars
- tails of comets
- eclipse simulation
- supernovae and novae simulation
- exoplanet locations
- ocular view simulation
- 3D sceneries
- skinnable landscapes with spheric panorama projection
customisability
- plugin system adding artifical satellites, ocular simulation, telescope control and more
- ability to add new solar system objects from on-line resources…
- add your own deep sky objects, landscapes, constellation images, scripts…
presentations
- G. Zotti gave a presentation about Virtual Archaeoastronomy with Stellarium (YouTube) for the Society for Cultural Astronomy in the American Southwest (SCAAS) on February 25th, 2023
- A. Wolf gave a presentation about Stellarium 1.0 (YouTube) at the Siberian Astronomical Forum SibAstro 2022 on September 25th, 2022
- A. Wolf gave a presentation about Stellarium — key changes in the last 5 years (YouTube) at the Siberian Astronomical Forum SibAstro 2021 on September 25th, 2021
- G. Zotti gave a presentation about Stellarium (YouTube) for the China-VO (Virtual Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences) on February 1st, 2021
- G. Zotti gave an invited talk (YouTube) at the IAU Symposium 367 on December 9th, 2020
- G. Zotti gave a talk about creating 3D sceneries (YouTube) at the TAG2016 Skyscapes session on December 20th, 2016
news
- Stellarium 24.2
- Stellarium 24.1
- Stellarium 23.4
- Stellarium 23.3
- Stellarium 23.2
- Stellarium 23.1
- Stellarium 1.2
- Stellarium 1.1
- D/L/Nakota and Ojibwe skycultures withdrawn
- Stellarium 1.0!
system requirements
minimal
- Linux/Unix; Windows 7 and above; macOS 11.0 and above
- 3D graphics card which supports OpenGL 2.1 and GLSL 1.3 or OpenGL ES 2.0
- 512 MiB RAM
- 600 MiB on disk
- Keyboard
- Mouse, Touchpad or similar pointing device
recommended
- 64-bit operating system
- Linux/Unix; Windows 10 and above; macOS 11.0 and above
- 3D graphics card which supports OpenGL 3.3 and above
- 1 GiB RAM or more
- 1.5 GiB on disk
- Keyboard
- Mouse, Touchpad or similar pointing device
- Moderately dark environment (deep shadow or indoors)
developers
Project coordinator: Fabien Chéreau
Graphic designer: Martín Bernardi
Developers: Alexander V. Wolf, Georg Zotti, Guillaume Chéreau, Ruslan Kabatsayev, Worachate Boonplod
Sky cultures researcher: Susanne M. Hoffmann
Collaborators: Jocelyn Girod
and everyone else in the community.
financial support
Many individuals and organizations are supporting the development of Stellarium by donations, and the most generous financial contributors (with donations of $250 or more) are Laurence Holt, Astronomie-Werkstatt "Sterne ohne Grenzen", John Bellora, Jeff Moe (Spacecruft), BairesDev, Vernon Hermsen, Triplebyte, Marla Pinaire, Satish Mallesh, Vlad Magdalin, Philippe Renoux, Fito Martin.
silver sponsor
social media
get involved
You can learn more about Stellarium, get support and help the project via these links:
- discussions
- mailing list
- wiki
- FAQ
- scripts
- landscapes
- 3D sceneries
- sky cultures
- documentation for developers
- scripting
- translations
- get support, report bugs, request new features
- all releases
- user guide
- weekly snapshots
- ppa for ubuntu linux
- archive
acknowledgment
If the Stellarium planetarium was helpful for your research work, please cite the following paper in your acknowledgment:
This research has made use of the Stellarium planetarium
- Zotti, G., Hoffmann, S. M., Wolf, A., Chéreau, F., & Chéreau, G. (2021). The Simulated Sky: Stellarium for Cultural Astronomy Research. Journal of Skyscape Archaeology, 6(2), 221–258. DOI: 10.1558/jsa.17822
Or you may download the BibTeX file of the paper to create another citation format.
Please note that the software has several releases since these fundamentals were published:
- Stellarium contributors (2024). Stellarium v24.2 Astronomy Software. URL https://stellarium.org/. DOI: 10.5281/zenodo.12506600
- Zotti, G., Wolf, A. (2022). Stellarium: Finally at Version 1.0! And Beyond. Journal of Skyscape Archaeology, 8(2), 332–334. DOI: 10.1558/jsa.25608
git
The latest development snapshot of Stellarium is kept on github. If you want to compile development versions of Stellarium, this is the place to get the source code.
books
Documentation and description of the sky cultures, state March 2022, plus a lot of additional research:
- Hoffmann, S. and Wolfschmidt, G. (2022, eds.). Astronomy in Culture - Cultures of Astronomy, Featuring the Proceedings of a splinter meeting in the German Astronomical Society. tredition, Ahrensburg.
supporters and friends
Stellarium is produced by the efforts of the developer team, with the help and support of the following people and organisations .